Poland is among the countries with the highest results for mathematics and science. The average scores of Polish 4th graders were higher compared to the results of 2019. Despite relatively good skill scores, positive attitudes towards mathematics and science as well as a sense of affiliation to the school community have been steadily declining.
The results of the TIMSS 2023 Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study were released on December 4. The report on Poland’s survey results was prepared by the Skills Research Unit of the of Educational Research Institute, responsible for conducting the study in Poland.
Download the national TIMSS 2023 report (PDF in Polish)
Press information download (PDF in Polish)
The most important findings of the study
Mathematics and science skills
- The average score of Polish fourth-graders in mathematics was 546 points, which gave Poland 10th place in the ranking. A significantly better score was recorded in 7 countries.
- The average score of Polish fourth-graders in science was 550 points, placing Poland in 7th place in the ranking. A significantly better score was recorded in only 4 countries.
- In Poland, the average score in 2023 increased in both science and mathematics compared to the score in 2019. The math score is higher than the one achieved in 2015, while the science score is similar.
- In each country, performance varies among pupils. In Poland, this variation is smaller than in most countries. The study distinguishes 5 levels of performance: advanced, high, medium, low and below low. These make it possible to describe pupils’ performance in terms of specific skills.
- In Poland, in both mathematics and science, the percentage of pupils with high skills (at an advanced or high level) increased compared to 2019. In contrast, the percentage of pupils achieving at or below a low level decreased compared to 2019 in both math and science. In the case of science, the results returned to the levels observed in 2015, while the percentage of pupils achieving low levels in math is the lowest among all editions of the survey to date.
- In most of the countries participating in the survey, including Poland, boys scored significantly higher than girls in mathematics. The average score of boys in Poland is 11 points higher than the average score of girls. The difference in the average scores of girls and boys, which was observed in 2019, has widened in 2023. In terms of natural science skills, as in 2019, no significant differences were observed between the average score of boys and girls.
- The average age of pupils taking part in the survey in Poland was 10.9 and was relatively high. Relationships are observed between the age of pupils taking the survey and skill scores. Countries where older children participated generally had higher scores on average.
Sense of affiliation to the school community and attitudes towards mathematics and science
- 60% of fourth-graders in Poland say they like going to school, a percentage that has steadily declined in successive editions of the study. Polish pupils’ sense of affiliation to their school, measured in 2023, is the lowest of all the countries participating in the survey.
- Increasingly fewer pupils in Poland like math and science – attitudes toward these subjects are steadily deteriorating. A decreasing proportion of fourth-graders like these subjects and find them interesting. The percentage of those particularly interested in math and science is also declining. Poland was among the countries with the least positive attitudes toward both math and science.
- Despite very good results in math and science, compared to other countries, Polish fourth-graders’ confidence in these subjects is at an average level. A large proportion of pupils believe that they are “just not good” at these subjects (as much as 41% for math and 37% for science).
Teachers – work experience and job satisfaction
- Teachers of fourth-graders in Poland are characterized by a very high level of work experience. The average length of service of mathematics teachers was as long as 24 years, and in science – as long as 25 years. The problems of the “aging” of the teaching staff and the lack of younger age groups entering the profession are progressing. In 2023, only 15% of fourth-graders had math and science teachers under the age of 40.
- In terms of the job satisfaction of math teachers, Poland ranked second to last, while in the case of science, it was last among 58 countries. Although Polish teachers’ declarations show that they like their work, find it inspiring and gives them a sense of meaning and satisfaction, their sense of pride in their profession and appreciation is much worse.
Involvement of parents in school activities
- Poland is among the top countries where parents are most likely to engage with their children in activities that prepare them for reading and math before they start school. Only six countries have a higher average rate of parental involvement in these activities. The results of the TIMSS survey indicate that parents’ undertaking activities with their children is associated with higher math and science skills. In Poland, parents with higher socioeconomic status report more frequent participation in activities with their children.
Average mathematics and science scores of pupils in the countries and regions participating in TIMSS 2023
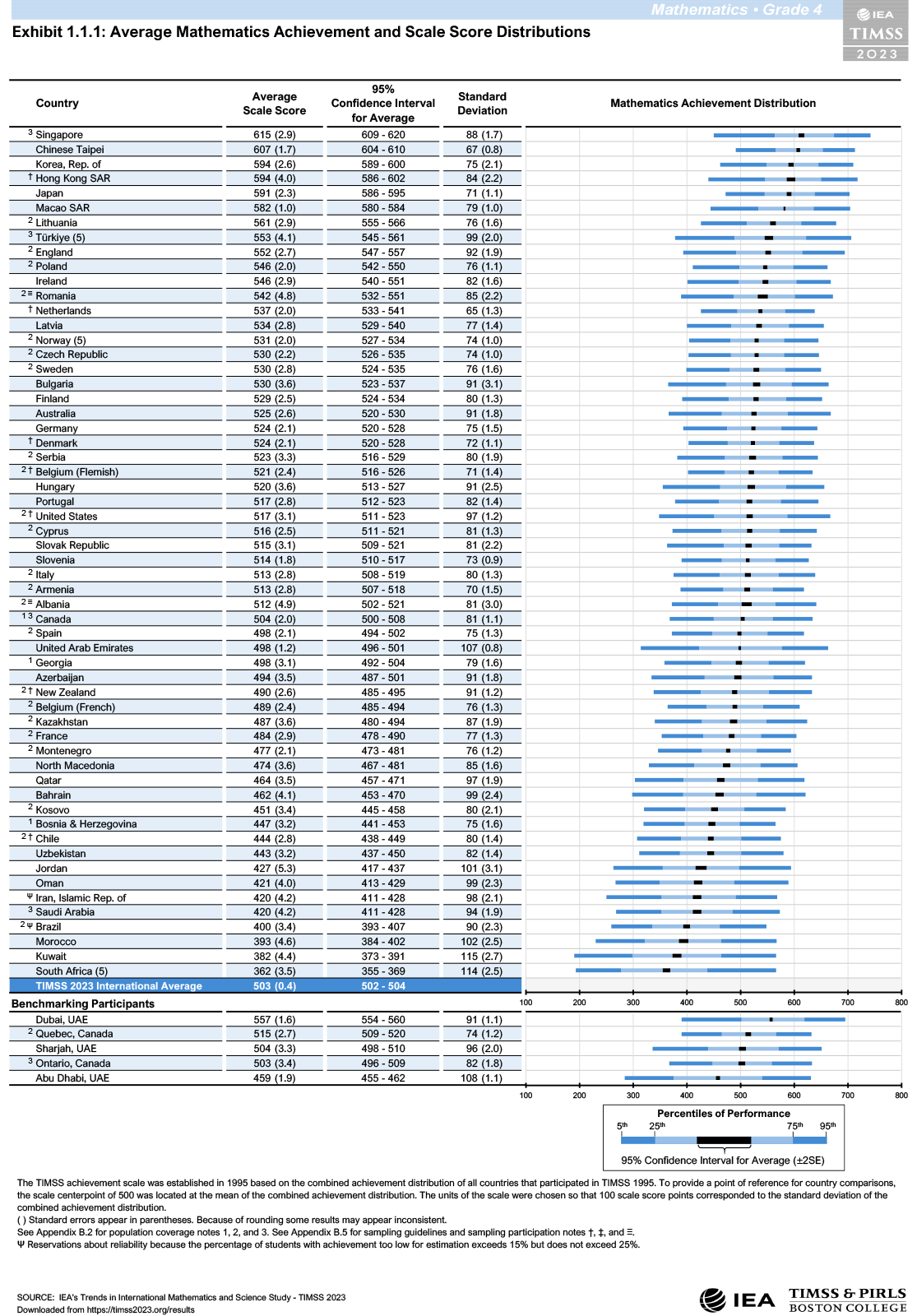
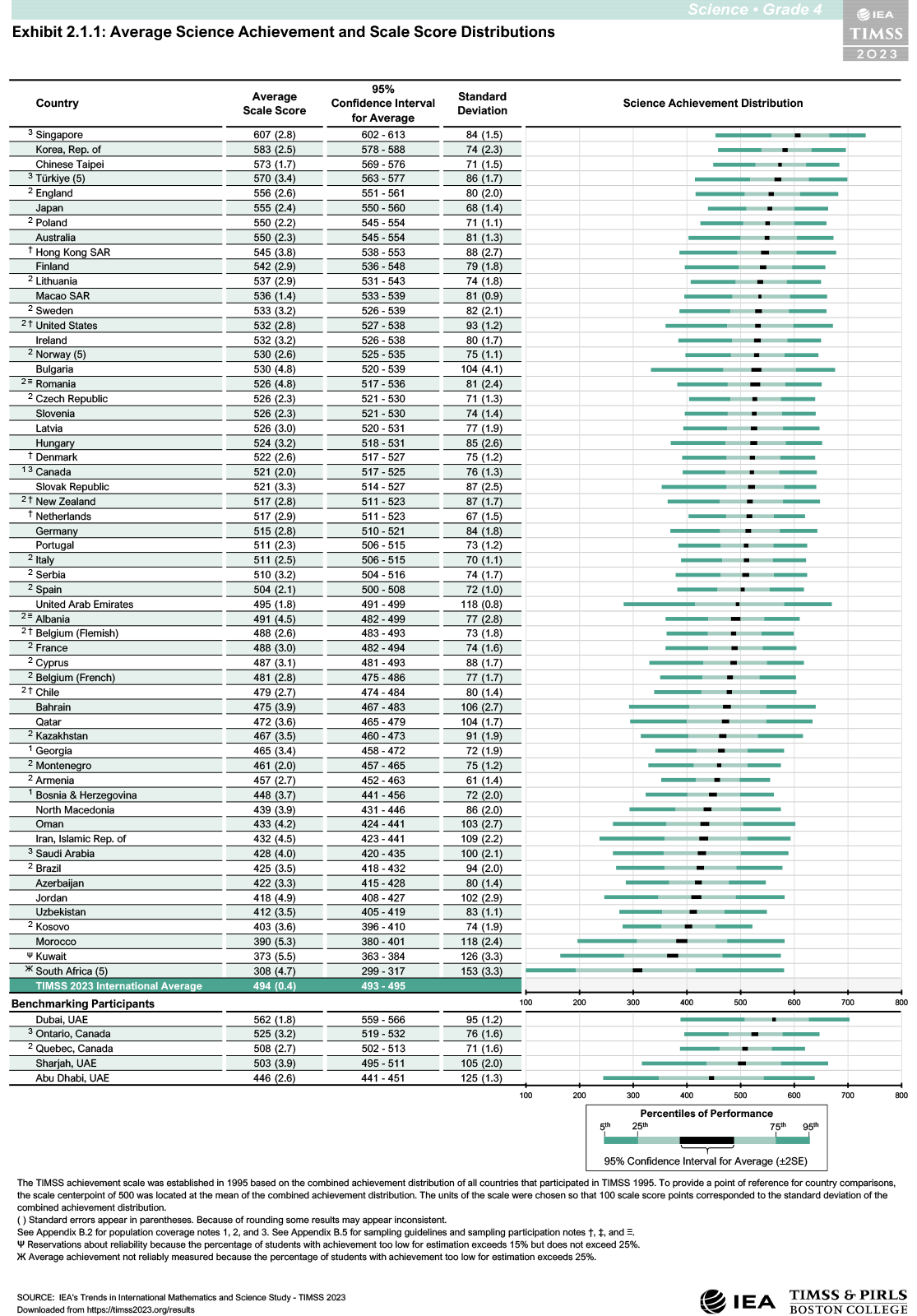
TIMSS (Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study) is one of the largest international comparative studies of mathematics and science learning. It was conducted in Poland among fourth-grade elementary school pupils in 2023. The objectives of the study are to provide data on pupils’ school achievement in mathematics and science, its variation by, among other things, gender and social background, information on changes in the level of such achievement and its variation, as well as on the conditions under which teaching and learning take place and the attitudes of pupils and teachers, which can provide a basis for explaining observed pupil performance.
TIMSS has been conducted every four years since 1995. Poland has been participating since 2011.


